Since version 1.5.3, Linux Deploy has begun work on integrating GNU/Linux containers with the Android environment. This opens up the following possibilities:
- access to the entire Android file system;
- execution of Android applications/commands directly from the container (for example, getprop, reboot, shutdown);
- switching between the container console and Android (
unchroot command).
The Linux Deploy project (LD for short) is now three years old, and here are some statistics. The current version of LD 1.5.2-160 is 52 releases and 160 updates, GitHub has 18,805 lines of code. More than 10,000 devices have been supported since Android 2.1. About 500 thousand installations. At the moment, LD supports 8 distributions (Debian, Ubuntu, Kali Linux, Fedora, Arch Linux, Gentoo, openSUSE, Slackware), for which installers and configurators are specially written. Each distribution supports from 2 to 9 architectures (varieties arm and x86, 32 and 64 bits) and from 1 to 7 releases. A total of 121 versions of distributions and their architectures are supported. Each distribution can be automatically configured to work with 1 of 5 supported desktop environments (XTerm, LXDE, Xfce, GNOME, KDE), not to mention SSH, VNC, and Xorg configurations. Taking into account the desktop environments (distribution/architecture/desktop environment), 597 installation options are obtained, which can be automatically deployed and configured via LD.
Modern models of mobile devices are equipped with a significant amount of RAM, for example, the ThL 5000 has 2 GB of RAM and 1 GB of swap memory. The Android system and system applications use no more than 1 GB of RAM. Thus, there is still at least 1 GB of memory that can be used for their own purposes. Linux Deploy version 1.5.1 adds support for installing GNU/Linux distributions in RAM.
One evening I decided to relax and made an animated version of the piglet for the Linux terminal, and then in JavaScript. The piglet itself is the logo of the networked open source intrusion detection and prevention system Snort.
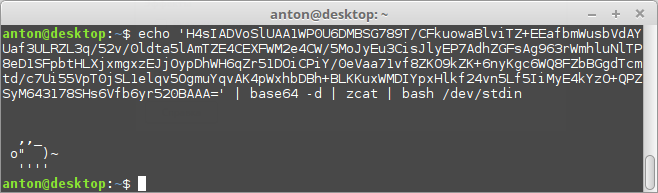
The code to run in the shell and the web version: https://github.com/meefik/piggy
Linux Deploy uses VNC as the default graphics subsystem, as the most native remote access to the GNU/Linux desktop system. However, you can configure remote access via the RDP protocol used in MS Windows operating systems. The example uses the Ubuntu 12.04 distribution (Precise Pangolin), but with minor changes this will work in other distributions. In this case, the RDP will run on top of the VNC server, so it is required that it be installed. In Linux Deploy, the VNC server is installed by default.
In addition to the graphical interface, Linux Deploy allows you to manage a GNU/Linux system instance from the command line via the Android terminal emulator. For these purposes, a special linuxdeploy script is used, which can be run from the Android command line and accepts the following parameters:
- prepare - Prepare a container, create an image, and create a file system;
- mount - Mount the container;
- umount - Unmount the container;
- install - Start the installation of a new system;
- configure - Launch the container reconfiguration;
- start - Launch the container;
- stop - Stop the container;
- shell - Execute chroot in a container;
- status - Information about the system.
Distributions running through Linux Deploy work with the Android kernel (a modified Linux kernel), and therefore you can change the configuration of the kernel or connect new modules only by rebuilding this kernel, or assembling modules for this version of the kernel.
Linux Deploy is designed to automatically install the latest versions of the most popular Linux distributions via the Internet and then run Linux applications of these distributions on Android. However, it also supports running the distribution from ready-made images. Prepared images of distributions can be downloaded from the Linux-on-Android project website.
The Kali Linux distribution is based on Debian and is positioned as a distribution for testing information security. Installation of this distribution in Linux Deploy is fully supported automatically with installation from the official repository (see the GNU/Linux installation instructions and the instructions at www.kali.org), but in some cases you may need to install from a ready-made image without Internet access.
Linux Deploy supports several graphics subsystems, graphics output options that can be used depending on the task.
VNC is used by default and is a software server that runs in parallel with Android and creates a virtual desktop to which you can connect through a special application — VNC-client. You can connect via VNC both locally, directly from the device, and remotely, for example, from a computer or other device. The only condition is that the devices are in the same subnet, for example, connected to the same router. VNC has two main parameters: server address and display number. The server address is the IP or host name where the VNC server is running. The display number is the number of the virtual desktop that we want to work with and on which the desktop environment runs. The display number is in the range from 0 to 99 and corresponds to the port number of the VNC server from 5900 to 5999, respectively, this port will be opened on the server to wait for the client to connect. VNC is easy to set up, there are many client applications, cross-platform, but not without its shortcomings. Such disadvantages include relatively low responsiveness of graphics, lack of support for hardware acceleration, lack of multitouch, additional load on the system and some others.

